2. Develop a program to solve simple computational problems using arithmetic expressions and use of each operator leading to simulation of a commercial calculator. (No built-in math
function)
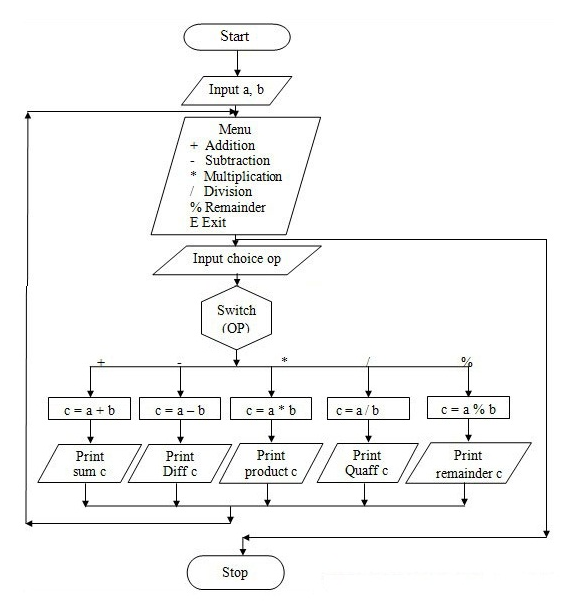
Algorithm:
Step 1: start
Step 2: read a and b variables
Step 3: display the options
Step 4: read input choice
Step 5: choice is 1 then goto step 6, or choice is 2 then goto step 7, or choice is 3 then goto step 8, or choice is 4 then goto step 9, or choice is other then these num goto step 10
Step 6: addition of two numbers
Step 7: subtraction of two numbers
Step 8: multiplication of two numbers
Step 9: division of two numbers.
Step 10: invalid choice
Step 11: print result
Step 12: stop
FLOWCHART:( click on image to zoom )
function)
Algorithm:
Step 1: start
Step 2: read a and b variables
Step 3: display the options
Step 4: read input choice
Step 5: choice is 1 then goto step 6, or choice is 2 then goto step 7, or choice is 3 then goto step 8, or choice is 4 then goto step 9, or choice is other then these num goto step 10
Step 6: addition of two numbers
Step 7: subtraction of two numbers
Step 8: multiplication of two numbers
Step 9: division of two numbers.
Step 10: invalid choice
Step 11: print result
Step 12: stop
FLOWCHART:( click on image to zoom )
PROGRAM:
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int a,b;
int op;
printf(" 1.Addition\n 2.Subtraction\n 3.Multiplication\n 4.Division\n 5.Remainder\n");
printf("Enter the values of a & b: ");
scanf("%d %d",&a,&b);
printf("Enter your Choice : ");
scanf("%d",&op);
switch(op)
{
case 1 :
printf("Sum of %d and %d is : %d",a,b,a+b);
break;
case 2 :
printf("Difference of %d and %d is : %d",a,b,a-b);
break;
case 3 :
printf("Multiplication of %d and %d is : %d",a,b,a*b);
break;
case 4 :
printf("Division of Two Numbers is %d : ",a/b);
break;
case 5:
printf("Remainder of %d and %d is : %d",a,b,a%b);
break;
default :
printf(" Enter Your Correct Choice.");
break;
}
}
OUTPUT:( click on image to zoom )

No comments:
Post a Comment